WAI-ARIA
Accessible Rich Internet Applications (WAI-ARIA) 1.0
Semantics is the science of meaning; in this case, used to assign roles, states, and properties that apply to user interface and content elements as a human would understand.
dynamic content and advanced user interface controls developed with Ajax, HTML, JavaScript
Using WAI-ARIA in HTML - Practical guide for developers on how to add accessibility information to HTML elements using the Accessible Rich Internet Applications specification.
ARIA Role, State, and Property Quick Reference
Definitions of States and Properties (all aria-* attributes)
WAI-ARIA 1.0 Authoring Practices - An author's guide to understanding and implementing Accessible Rich Internet Application.
Roles
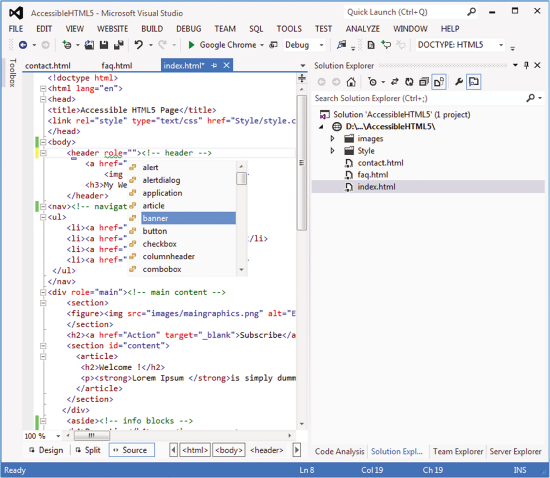
A WAI-ARIA role is set on an element using a role attribute.
<li role="menuitem">Open file…</li>
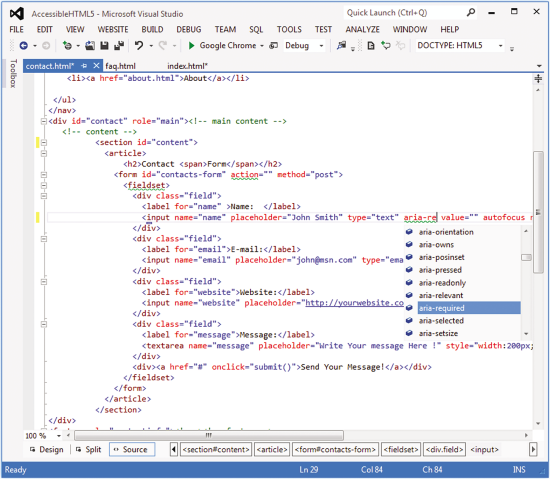
States & Properties
the values of properties (such as aria-labelledby) are often less likely to change throughout the application life-cycle than the values of states (such as aria-checked) which may change frequently due to user interaction
<li role="menuitemcheckbox" aria-checked="true">Sort by Last Modified</li>
Use ARIA attributes to control styling:
CSS attribute selectors.
[aria-invalid=true] {border : 2px solid red;}
Accessible Name
The name of a user interface element. The value of the accessible name may be derived from a visible (e.g., the visible text on a button) or invisible (e.g., the text alternative that describes an icon) property of the user interface element.
A simple use for the accessible name property may be illustrated by an "OK" button. The text "OK" is the accessible name. When the button receives focus, assistive technologies may concatenate the platform's role description with the accessible name. For example, a screen reader may speak "push-button OK" or "OK button". The order of concatenation and specifics of the role description (e.g. "button", "push-button", "clickable button") are determined by platform accessibility APIs or assistive technologies.
Landmark

A type of region on a page to which the user may want quick access. Content in such a region is different from that of other regions on the page and relevant to a specific user purpose, such as navigating, searching, perusing the primary content, etc.
Live Region
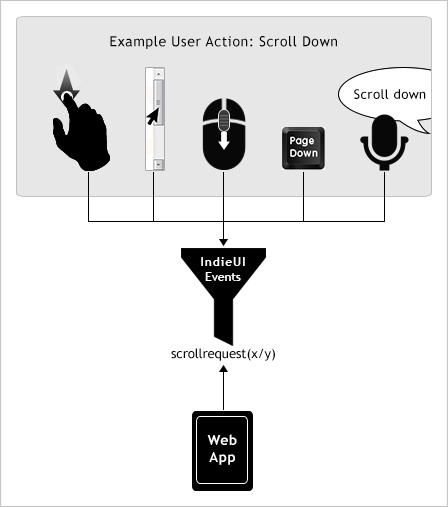
Live regions are perceivable regions of a web page that are typically updated as a result of an external event when user focus may be elsewhere.
Examples of live regions include a chat log, stock ticker, or a sport scoring section that updates periodically to reflect game statistics.
aria-live, aria-relevant, aria-atomic, and aria-busy
Widget
Discrete user interface object with which the user can interact. Widgets range from simple objects that have one value or operation (e.g., check boxes and menu items), to complex objects that contain many managed sub-objects (e.g., trees and grids).
Widget Roles
The following roles act as standalone user interface widgets or as part of larger, composite widgets.
The following roles act as composite user interface widgets. These roles typically act as containers that manage other, contained widgets.
Document Structure
The following roles describe structures that organize content in a page. Document structures are not usually interactive.
Landmark Roles
The following roles are regions of the page intended as navigational landmarks.
Global States and Properties
The following global states and properties are supported by all roles and by all base markup elements.
Widget Attributes
This section contains attributes specific to common user interface elements found on GUI systems or in rich internet applications which receive user input and process user actions. These attributes are used to support the widget roles .
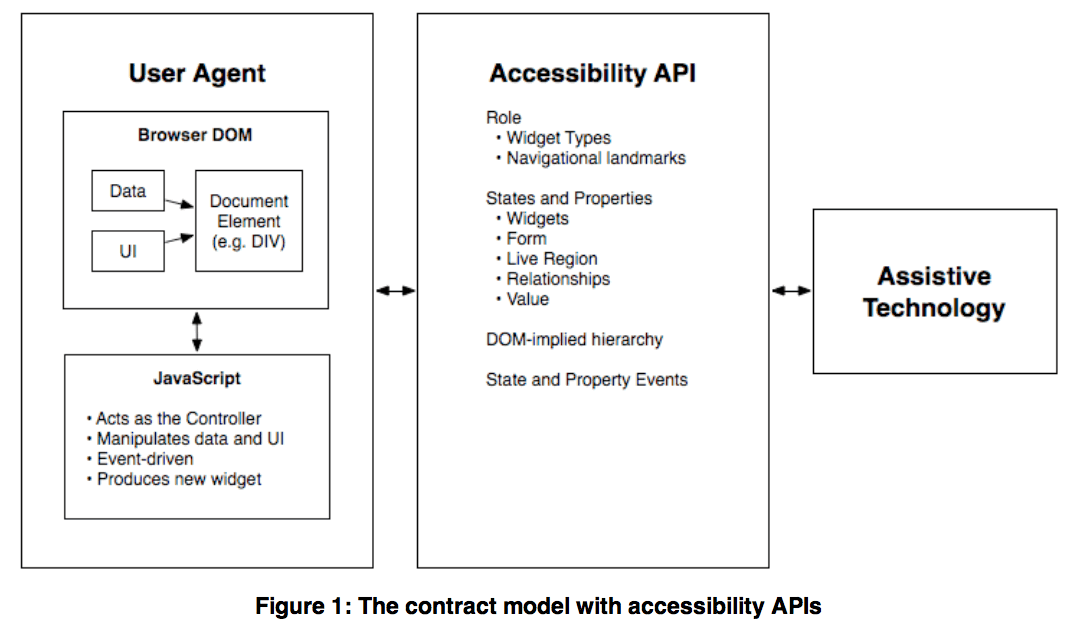
Widget attributes might be mapped by a user agent to platform accessibility API states, for access by assistive technologies, or they might be accessed directly from the DOM. User agents MUST provide a way for assistive technologies to be notified when states change, either through DOM attribute change events or platform accessibility API events.
Live Region Attributes
This section contains attributes specific to live regions in rich internet applications. These attributes may be applied to any element. The purpose of these attributes is to indicate that content changes may occur without the element having focus, and to provide assistive technologies with information on how to process those content updates. Some roles specify a default value for the aria-live attribute specific to that role. An example of a live region is a ticker section that lists updating stock quotes.
- aria-atomic
- aria-busy (state)
- aria-live
- aria-relevant
Drag-and-Drop Attributes
This section lists attributes which indicate information about drag-and-drop interface elements, such as draggable elements and their drop targets. Drop target information will be rendered visually by the author and provided to assistive technologies through an alternate modality.
- aria-dropeffect
- aria-grabbed (state)
For more information about using drag-and-drop, see Drag-and-Drop Support in the WAI-ARIA Authoring Practices ([ARIA-PRACTICES]).
Relationship Attributes
This section lists attributes that indicate relationships or associations between elements which cannot be readily determined from the document structure.
- aria-activedescendant
- aria-controls
- aria-describedby
- aria-flowto
- aria-labelledby
- aria-owns
- aria-posinset
- aria-setsize
- Pick the widget type (role) from the WAI-ARIA taxonomy
- From the role, get the list of supported states and properties
- Establish the widget structure in the markup (parent/child)
- Repeat steps 1-3 for the children of the parent
- Establish keyboard navigation of the widget and plan for how it will be navigated to within the document
- Apply and manage needed WAI-ARIA states in response to user input events
- Synchronize the visual UI with accessibility states and properties for supporting user agents
- Showing and Hiding Sections in a Widget
- Support basic accessibility, such as alternative text on images
- Establish WAI-ARIA relationships between this widget and others
- Review widget to ensure that you have not hard coded sizes
- Compensate for Background Images when in High Contrast Mode
- Test with User agent, Assistive Technology, and People with disabilities
- Set tabindex="0" to the current active descendant in the widget while setting tabindex="-1" on all the other child elements of the widget
- As the user navigates (e.g. arrows) away from an item, the old item gets a tabindex="-1" and the new item gets tabindex="0".
- Use the javascript method to set focus, using its JavaScript focus() method, on the item whose tabindex="-1"
Reusable Component Libraries
Rich internet applications are complex to author. To save time, it is often faster to use existing widget libraries that implement WAI-ARIA and that have already gone through:
- extensive assistive technology testing
- cross browser testing
- testing to ensure that the widgets respond to desktop settings
- testing to ensure that the widgets match a common keyboard style guide
Some publicly available UI component libraries have already implemented WAI-ARIA. Authors can reuse such libraries to start developing accessible rich internet applications.